High voltage surge stoppers ensure reliable operation during power surges
In systems where power is distributed over long wires, severe transients are generated by load steps (abrupt changes in load current). Negative load steps happen when load current drops from a high value to a low value. Negative changes in current (dI/dt) cause the wire’s parasitic inductance to generate a positive-going high voltage spike which can cause damage to neighboring devices powered from the same wire. High values of dI/dt are produced by fast load switching, such as caused by relays, switch contacts and solid state load switching. Corroded connections between a power source and load can lead to an abrupt interruption of current flow, and a high value of dI/dt. The best example of this condition is automotive load dump, where there is a sudden break in the connection to the battery caused by vibration and corroded terminals.
Load dump causes a voltage surge that stays elevated for hundreds of milliseconds (see Figure 1). The amplitude of the transient, according to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), may be as high as 125V. A typical load dump profile has a rise time of 5 milliseconds and decays exponentially with a time constant of 200ms. In industrial systems similar events can be caused by regeneration in solenoids and motors.

Figure 1: Typical Load Dump Waveform
Electronic circuits have become more prevalent in automobiles, and they must be reliable. In addition, sophisticated consumer electronics such as smart phones, laptops, MP3 players, GPS, and data entry devices that charge through automobile cigarette lighters must also protect their products from both repetitive transients and unexpected voltage spikes. Inadequate protection from high voltage transients leads to degraded performance or failure and costly replacement.
These transients pose a difficult challenge for engineers focused on protecting sensitive electronics. Historically, this protection was achieved using bulky capacitors, TVS diodes and fuses, but this discrete solution consumes a lot of real estate, and may be impractical.
Linear Technology first released the LT4356 Surge Stopper in 2007 to address these challenges. The LT4356 operates from 4V to 80V and provides -60V of reverse protection on the input pins. During an overvoltage transient, the output clamps to a user-defined voltage, defined by the resistor divider network on the output. The LT4356 is capable of suppressing surges >100V as long as a resistor and TVS diode is used at the input to avoid exceeding the absolute maximum operating voltage (see Figure 2). Because the current sensing circuitry is upstream of the MOSFET, overcurrent protection must be disabled if the device is used to protect from transients above 100V.

Figure 2: LT4356 Withstands 150V at Input
Two new devices have recently been added to Linear Technology’s surge stopper family, the LTC4366 High Voltage Floating Surge Stopper and the LT4363 High Voltage Surge Stopper with Overcurrent Protection. The LTC4366 is designed for systems that continuously operate at voltages above 100V, or where protection from extremely high voltage transients (>200V) is required (see Figure 3).


Figure 3: LTC4366 High Voltage Floating Surge Stopper
The LT4363 is a second generation version of the popular LT4356, moving the overcurrent sensing downstream of the pass FET so that it provides overcurrent protection while withstanding voltage transients greater than 100V (Figure 4).
However, like the LT4356, the absolute maximum rating for the LT4363 is 100V, so the input must be protected from high voltage transients >100V using a resistor and TVS diode as shown in Figure 3. In contrast, the LTC4366 uses a floating topology; external voltage dropping resistors allow it to float up with the supply, isolating it from the high voltage surge. The upper limit on the operating voltage is only limited by the availability of the high valued resistors and sizing the MOSFET to handle the power dissipated during voltage regulation.

Figure 4: LT4363 High Voltage Surge Stopper with Overcurrent Protection
Features & Benefits:
The LT4363 and LTC4366 share some common features. A list of the features offered by these devices and their respective benefits are described here:
Wide Operating Range:
- The LT4363 offers a wide operating range (4V to 80V), offering continuous operation under cold crank conditions where the battery voltage can be as low as 4V. The LT4363 can also be used as a wide operating range Hot Swap™ controller. The device can withstand overvoltage transients greater than 100V if a TVS diode and resistor are used to protect the device from exceeding its 100V abs max rating.
- The LTC4366 operating range extends from 9V to >500V, enabling extremely high voltage operation using a floating topology. The operational upper voltage is limited only by the availability of high valued resistors and MOSFET ratings. While the LTC4366 cannot be used for cold crank applications, there are many automotive systems that do not need to be operational during ignition (Infotainment, GPS).
Well Regulated Overvoltage Protection
- Protects valuable, safety critical electronics downstream from the device. The adjustable well-regulated output clamp voltage provides flexibility to control the clamped voltage level at the output while riding out the transient. For low voltage applications, this eliminates the need for high voltage rated components downstream, thus saving costs. The LT4363 also offers OV and UV comparator inputs which inhibit auto-retry if the input voltage is outside the range of these adjustable thresholds. Both the LT4363 and LTC4366 offer long cooldown periods between auto-retry. This helps reduce the power dissipated in the external pass FET during faults.
Adjustable Fault Timer
- LT4363/LTC4366 offer an adjustable fault timer which limits power dissipation on the pass FET. During a fault condition the LT4363/LTC4366 uses a current source to charge the capacitor on the TIMER pin. This allows the flexibility to use lower rated SOA MOSFETs. No competitive overvoltage products offer an adjustable timer.
Fault Output Indicator
- The LT4363 offers a fault output to provide advance warning of impending power-off due to an overvoltage or overcurrent fault condition.
Overcurrent Protection
- The LT4363 features an adjustable current limit that protects against short circuits or excessive load current. Voltage drop is monitored across an external current sense resistor on the output to protect against overcurrent faults. During an overcurrent event, the GATE pin is regulated to limit the current through this resistor. Charging of the TIMER pin is accelerated with increasing voltage across the MOSFET. This turns the MOSFET off faster, since more power is dissipated during this condition.
Inrush Current Limiting
- Eliminates current spikes propagating through the MOSFET to the output during power-up by controlling the GATE pin slew rate.
Reverse Input Protection to -60V
- The LT4363 is designed to withstand reverse voltage of up to -60V without damage to itself or the load (using back-to-back FET). This eliminates the need for a blocking diode which causes extra power loss, generates heat, and reduces the available supply voltage range. During cold crank, the extra voltage drop is particularly undesirable.
Low Shutdown Current (<20uA)
- Prevents automobile battery from discharging when parked for long periods. Offers additional power savings for improved battery life in portable applications.
Strong Gate Sink Current
- Strong current pull-down (>150mA) on the GATE during a fault ensures fast response time.
-40oC to +125oC Operating Range
- High Temperature rating allows operation in automotive and industrial applications. Contact Linear Technology for details on -55oC military plastic versions.
Target Markets:
Linear Technology’s surge stopper products have wide appeal for the industrial, avionics and automotive markets due to their ability to provide solid high voltage front-end protection in a very small solution size.
LTC4366 applications include fuel cells, industrial and military systems, and high voltage DC distribution in servers.
LT4363 applications include all consumer, automotive, industrial, avionics, communications, and military applications that operate from a battery or a badly behaving supply.
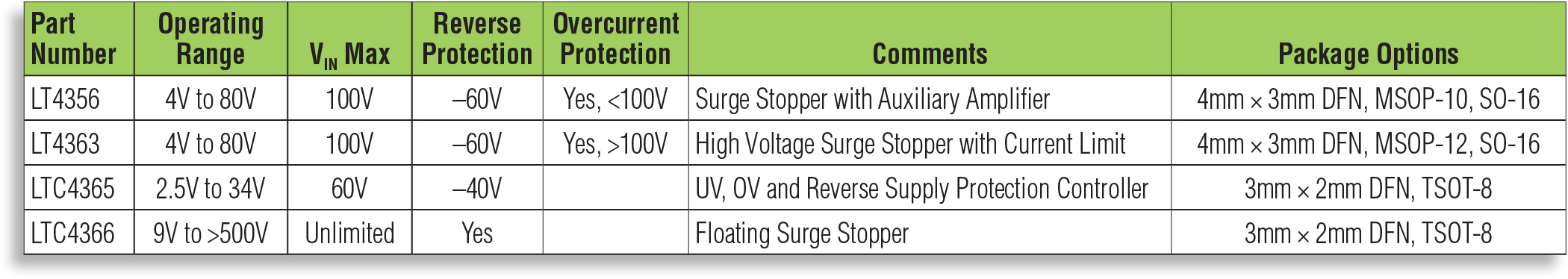
Table 1: Linear Technology’s High Voltage Surge Stopper Family. For full resolution click here.
 If you enjoyed this article, you will like the following ones: don't miss them by subscribing to :
eeNews on Google News
If you enjoyed this article, you will like the following ones: don't miss them by subscribing to :
eeNews on Google News



